| HOME | HELP | FEEDBACK | SUBSCRIPTIONS | ARCHIVE | SEARCH | TABLE OF CONTENTS |
(none)
|
| ||||||||
(none) | |||||||||
|
|
Animal Improvement Programs Laboratory, Agricultural Research Service USDA, Beltsville, MD 20705-2350
Corresponding author:
G. R. Wiggans; e-mail:
wiggans@aipl.arsusda.gov.
A method to detect and to adjust or exclude abnormally low
or high milk, fat, and protein yields on test-day (TD) was
developed. Predicted TD yield is calculated based on preceding and
subsequent (if available) TD yields. Observed TD yields that are
<60% or >150% of predicted TD yield are defined as abnormal.
Most abnormal yields are adjusted to this floor or ceiling, but
some are excluded. Yields of <4.5 kg that are identified as
from a cow that was sick or that are less than half the mean of
adjacent tests are excluded as are yields of >59 kg above
predicted yield. Lactation yields are calculated from the restricted
TD yields. When this procedure was applied to 2002 data, 1.8% of
milk, 2.4% of fat, and 1.6% of protein yields on TD were below
the acceptance range and 0.1% of milk and protein and 0.8% of
fat were above. Predicted TD yield was calculated as preceding
TD yield plus preceding test interval multiplied by daily yield
change (slope) based on days in milk (DIM), DIM2, previous
normal TD yield, and interaction between DIM and previous TD
yield. To accommodate changes in slope at peak yield, separate
coefficients were estimated for <50 and 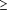 50 DIM. Herd mean was used
when only one TD was recorded for a cow (or when two were recorded
and the second was designated as abnormal based on the first) and to
determine an acceptable range for component percentages. Predicted TD
yield for first TD was based on subsequent rather than previous
normal TD. To test the adjustments, lactation records with one
abnormal TD yield or more were matched with subsequent lactation
records. Correlation between consecutive lactations increased from
0.692 to 0.693 for milk (561,063 lactation pairs), from 0.653 to
0.660 for fat (951,387 lactation pairs), and from 0.686 to 0.694 for
protein (488,653 lactation pairs). Outlier adjustment improved the
correlation between consecutive lactation yields and is applied
routinely to TD records of cows for calvings since 1997.
50 DIM. Herd mean was used
when only one TD was recorded for a cow (or when two were recorded
and the second was designated as abnormal based on the first) and to
determine an acceptable range for component percentages. Predicted TD
yield for first TD was based on subsequent rather than previous
normal TD. To test the adjustments, lactation records with one
abnormal TD yield or more were matched with subsequent lactation
records. Correlation between consecutive lactations increased from
0.692 to 0.693 for milk (561,063 lactation pairs), from 0.653 to
0.660 for fat (951,387 lactation pairs), and from 0.686 to 0.694 for
protein (488,653 lactation pairs). Outlier adjustment improved the
correlation between consecutive lactation yields and is applied
routinely to TD records of cows for calvings since 1997.
Key Words: test day · abnormal yield · outlier detection · yield adjustment
Abbreviations: TD = test day
| HOME | HELP | FEEDBACK | SUBSCRIPTIONS | ARCHIVE | SEARCH | TABLE OF CONTENTS |